Excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis, can be a constant source of self-consciousness and discomfort for both men and women. For those who experience it, sweating beyond what is necessary to regulate body temperature can affect not just their physical comfort but also their confidence and quality of life. At PLSTK, we offer Botox as an effective treatment for excessive underarm sweating, providing relief from this condition and helping individuals regain their confidence and peace of mind.
What Causes Excessive Sweating in the Underarms?
Sweating is a natural bodily function that helps regulate body temperature by releasing moisture to cool the skin. However, for some individuals, the sweat glands are overactive, leading to excessive sweating in certain areas, particularly the underarms. This condition, called axillary hyperhidrosis, occurs when the sweat glands in the underarms produce more sweat than the body actually needs.
The exact cause of excessive sweating is not always clear, but it can often be classified into two categories:
- Primary Hyperhidrosis: This is the most common form of excessive sweating, where no underlying medical condition is causing the excessive sweating. It’s often triggered by factors like heat, stress, or physical exertion. The overactive sweat glands in the underarms begin to produce excessive moisture even when the body doesn’t need it.
- Secondary Hyperhidrosis: In some cases, excessive sweating is a symptom of an underlying condition, such as hormonal imbalances, infections, or certain medications. However, for most people with excessive underarm sweating, the cause is primary hyperhidrosis, and the condition can persist for years without any other symptoms.
Excessive underarm sweating can significantly impact an individual’s life, causing discomfort, embarrassing stains on clothing, and a constant worry about odor. It can also take a toll on a person’s self-esteem, leading them to avoid certain activities or situations where they feel their condition might be noticed.
How Botox Works to Treat Excessive Sweating
Botox is most commonly recognized for its ability to smooth wrinkles, but it is also an effective treatment for excessive sweating. Botox works by temporarily blocking the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, preventing them from producing sweat in the treated areas.
When injected into the underarms, Botox blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals the sweat glands to produce sweat. By inhibiting these signals, Botox prevents the sweat glands from overproducing moisture, effectively reducing or even eliminating sweating in the area.
While not a permanent solution, this treatment is highly effective for most individuals and offers significant relief from excessive sweating for several months.
What to Expect from Botox Treatment for Excessive Sweating
The Botox treatment for excessive sweating in the underarms is a simple and quick procedure that can be done in-office with minimal downtime.
- Consultation: Your provider at PLSTK will start with a consultation to assess your sweating concerns and determine if Botox is the right treatment for you. They will discuss your medical history, any underlying conditions, and your specific goals for treatment.
- Preparation: The underarm area will be cleaned, and in some cases, a topical numbing cream may be applied to minimize any discomfort during the injections. Although the injections are relatively quick, numbing can help make the process more comfortable.
- Injection: Botox will be injected into the underarm area. The procedure typically takes only about 10 to 15 minutes, depending on the extent of the area being treated. You may feel a small pinch with each injection, but the procedure is generally well-tolerated by most individuals.
- Post-Treatment: After the injections are complete, you’ll be able to resume most of your normal activities. There’s no need for any bandages or lengthy recovery time. The area will be monitored for any immediate reactions, but you’ll likely be able to go about your day without any noticeable side effects.
What to Expect After Botox Treatment for Excessive Sweating
- What To Expect Immediately After Treatment: Some patients may experience mild soreness or swelling at the injection site, but this typically goes away within a few hours to a day. You may also notice some redness, but this should subside quickly.
- Avoid Rubbing or Massaging the Area: After the treatment, it’s important to avoid rubbing or massaging the underarm area for at least 24 hours. This helps ensure that the Botox stays in the targeted area and doesn’t spread to unintended areas.
- Avoid Intense Exercise: It’s best to avoid intense physical activity or exercise for at least 24 hours after the treatment to prevent excessive sweating or irritation of the treated area.
- Results Over Time: You may begin to notice a reduction in sweating within a few days of the treatment. Full results typically appear within 1 to 2 weeks, as the Botox takes effect and the sweat glands become less active. The reduction in sweat production can be significant, with some individuals experiencing a near-complete cessation of underarm sweating.
When to Expect Results
The effects of Botox for excessive sweating typically begin within 3 to 5 days, with the full benefits becoming evident after about 7 to 10 days. Most individuals experience a significant reduction in underarm sweating, with many seeing near-complete dryness in the treated area.
The effects of Botox are temporary, with the results generally lasting between 4 to 6 months. Over time, the body metabolizes the Botox, and the sweat glands will begin to function as they did before the treatment. However, the results can be maintained with regular follow-up treatments. Many clients find that after a few rounds of Botox, the frequency of treatments may decrease as the sweat glands remain less active.
Aftercare Advice
- Avoid Touching the Treated Area: Avoid rubbing or massaging the underarm area for at least 24 hours after treatment to allow the Botox to settle properly.
- Limit Strenuous Activities: Refrain from intense physical activity, such as exercise, heavy lifting, or yoga, for at least 24 hours after the procedure. This will prevent excessive sweating and help the Botox stay in place.
- No Heat Exposure: Avoid saunas, hot tubs, or excessive heat for the first 24 to 48 hours to reduce swelling and ensure the Botox doesn’t migrate from the treated area.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water after the treatment can help support the natural detoxification process in your body.
A Confidence-Boosting Solution for Excessive Sweating in Brooklyn
Botox for excessive sweating in the underarms is a safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment that can significantly improve quality of life by reducing discomfort and boosting confidence. With results that typically last for several months and a treatment process that is quick and well-tolerated, Botox offers a reliable solution for both women and men struggling with hyperhidrosis.
At PLSTK in Greenpoint, we are committed to helping our clients feel their best, both physically and emotionally. If you’re struggling with excessive sweating and want to learn more about Botox as a treatment option, call 877-697-5785 today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward a more confident, sweat-free you.
Many times, I have asked myself, “Do I sweat too much?” But where do you draw the line between normal and excessive sweating, exactly? As it turns out, hyperhidrosis, the medical term for excessive sweating, is more common than you might think, especially if you’re one of the people who are afraid that they sweat more than other people around them. What’s more, hyperhidrosis is surprisingly easy to treat.
What is hyperhidrosis, exactly?
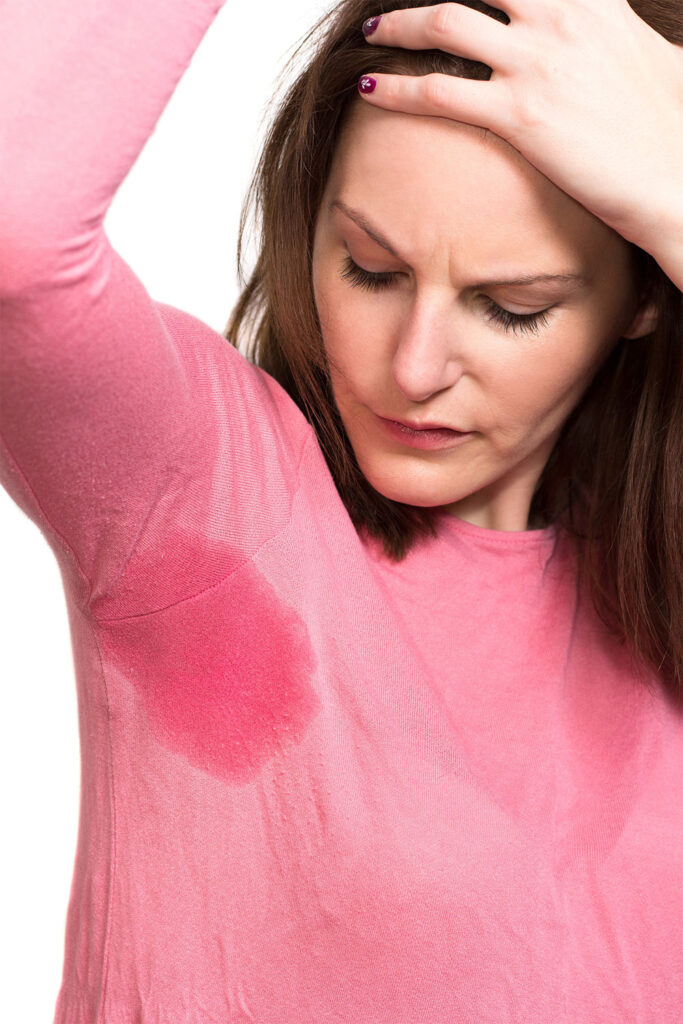

Primary hyperhidrosis
The most common type is primary hyperhidrosis, which has no known underlying physical cause. “Primary hyperhidrosis is due to overactive signaling of sweat glands to secrete sweat without stimuli. In other words, your body starts sweating without any explicable reason (like feelings of anxiety, hot temperatures, or exercise). This kind of hyperhidrosis can occur at any given time or during any season of the year, even if the person is not physically warm or is completely at rest. Primary hyperhidrosis is most commonly seen in the underarms, palms, and soles of the feet.
Secondary hyperhidrosis
Secondary hyperhidrosis, on the other hand, is excessive sweating that’s caused by an external factor such as medication or illness, like a tumor, diabetes, or thyroid issues.
What’s the difference between normal vs. excessive sweating?
Of course, the next question then becomes: What’s the threshold between normal and worrisome sweat levels? Are there any other symptoms to look out for that don’t involve perspiration?
Excessive sweating, or how someone perceives it, is very personal in that what might be excessive to you is normal or not troubling to somebody else.
Because sweat is not really a quantifiable thing, like blood pressure, it’s really complicated to measure someone’s sweat levels throughout any given day. It’s hard to define exactly what hyperhidrosis is, but it could be something along the lines of increased amounts of sweating, which causes social or personal embarrassment, withdrawal, and/or avoidance behavior.
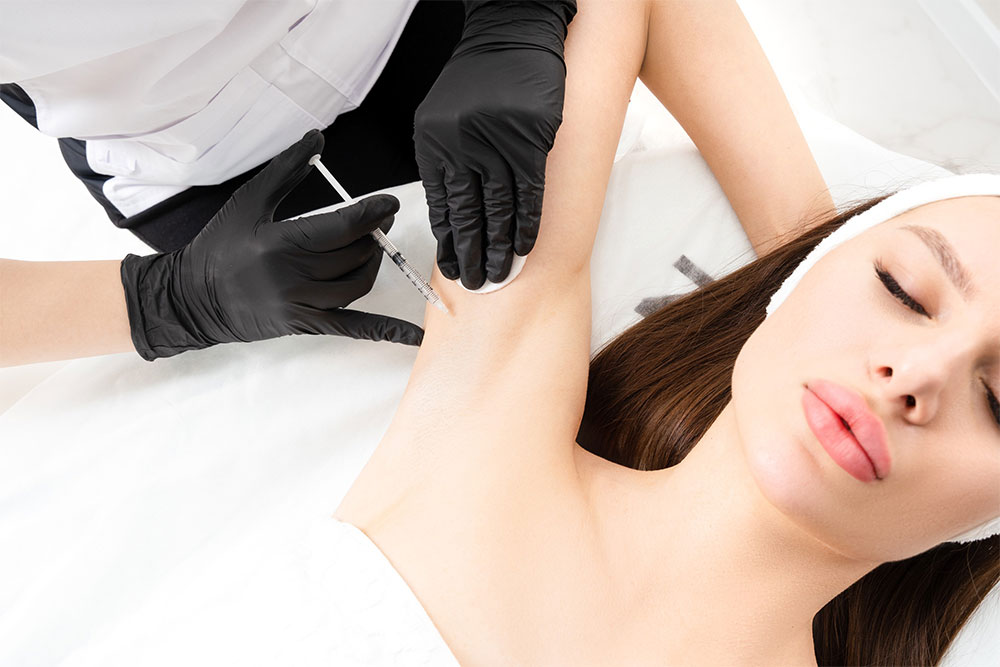
How is hyperhidrosis treated?
Good news: There are many hyperhidrosis treatment options, including topical creams, injections, and oral medications. What your physician prescribes will likely depend on the area where you’re experiencing hyperhidrosis as well as the severity.
Botox therapy. Yes, the very same injectable that you might get to prevent wrinkles between your brows can also help stop excessive sweating. Experts agree that Botox is most effective in the underarm area, where it can work for up to six months. On other areas of the body, however, such as the hands and feet, Botox isn’t the best line of treatment because it’s both painful and only lasts two to three months.
